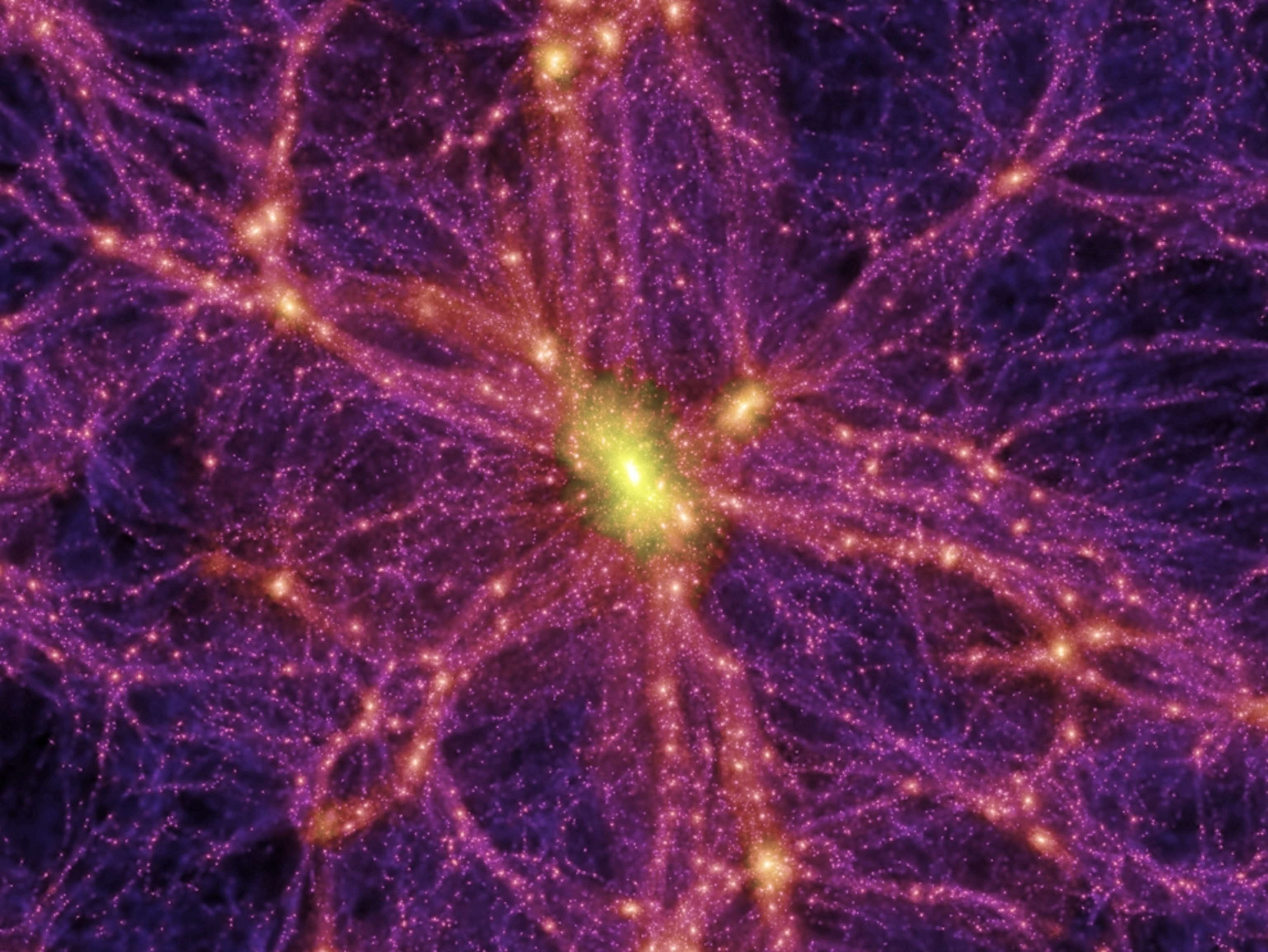
Dark energy is a fascinating and enigmatic force that shapes our understanding of the universe’s expansion. Recent findings from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) collaboration, which includes researchers from Harvard, suggest that dark energy, often regarded as a cosmological constant, may be evolving over time. This development raises critical questions about the framework of dark energy evolution and indicates that the future state of our dark energy universe could be different than previously thought. As scientists delve into the intricate relationship between matter and dark energy, leveraging vast data sets and sophisticated analysis, the implications for our cosmic knowledge are profound. The DESI dark energy project, encompassing a global network of over 900 researchers, is poised to redefine our understanding of the cosmos through groundbreaking insights into the nature and role of dark energy in shaping the fabric of our universe.
The concept of dark energy refers to a mysterious component driving the accelerated expansion of our universe. Often described in terms of the cosmological constant, this elusive energy category is now being scrutinized through modern research techniques. The evolution of dark energy and its influence on cosmic phenomena, such as the distribution of galaxies, are critical topics under investigation. As initiatives like DESI continue to collect extensive astronomical data, researchers are progressively uncovering the intricacies of our universe’s expansion dynamics. This exploration not only enhances our grasp of cosmic forces but also prompts essential updates in our theoretical understanding, as suggested by ongoing cosmological constant updates emerging from various studies.
Understanding Dark Energy and Its Evolution
Dark energy is a mysterious force that dominates the universe’s expansion. Traditionally viewed as a constant force influencing cosmic growth, recent investigations, particularly from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) collaboration, suggest that dark energy might not remain static. Instead, evidence points to its evolution—weakening over time—which could drastically reshape our understanding of cosmic dynamics and potentially signal the need for a revision of the current cosmological models we rely on.
As researchers delve deeper into the nature of dark energy, they are employing substantial datasets to analyze its historical effects. Through extensive mapping of over 14 million galaxies and quasars, scientists are uncovering nuances in how dark energy interacts with matter across the vast expanse of the universe. These findings indicate that the behavior of dark energy may not only be complex but also pivotal in determining the ultimate fate of the universe.
Insights from DESI: Dark Energy’s Role in Cosmology
The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) stands as a monumental effort in modern astrophysics, enlisting over 900 researchers from more than 70 institutions. By tracking luminous galaxies and quasars, DESI effectively captures the influence of dark energy over an extensive timeline, enabling scientists to create the largest 3D map of the universe. This mapping showcases how dark energy interplays with the distribution of matter, providing essential insights into its role in our cosmic evolution.
Analysis from DESI suggests that the effects of dark energy are evolving, posing significant implications for our current universe models. By examining standards of measurement defined by Baryon Acoustic Oscillations, researchers can determine the varying strengths of dark energy across different epochs. This progression aids in refining cosmological parameters and supports ongoing discussions about potential updates to the cosmological constant, suggesting the universe’s destiny could be shaped by an ever-changing balance of forces.
The Collaboration’s Technological Impacts on Dark Energy Research and Cosmology Trends in Dark Energy Discoveries
Frequently Asked Questions
What is dark energy and how does it affect the universe?
Dark energy is a mysterious force that is responsible for the accelerated expansion of the universe. It is believed to make up around 68% of the universe, acting as a counterbalance to gravity. The study of dark energy evolution helps scientists understand how this force influences the overall dynamics of the cosmos.
How is dark energy related to the cosmological constant?
Dark energy is often associated with the cosmological constant, which is a theory proposing that dark energy remains constant throughout time. Recent findings suggest that this constant may actually be changing, prompting researchers to consider potential updates to our understanding of the dark energy universe.
What recent advancements have been made in the study of dark energy using DESI?
The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) has made significant strides in mapping the impact of dark energy by analyzing data from over 14 million galaxies and quasars. This research, particularly the analysis of baryon acoustic oscillations, provides crucial insights into how dark energy has evolved over the past 11 billion years.
What are the implications of the findings from the DESI dark energy analysis?
The DESI dark energy analysis indicates that dark energy may be evolving in ways not previously understood. This has serious implications for our current models of cosmology and suggests that the future of the universe may look different than previously anticipated.
How can the data from DESI advance our understanding of dark energy?
Data from DESI provides an unprecedented look at the universe’s structure and the distribution of galaxies, which are essential for understanding dark energy’s role. This information will help astronomers refine their models regarding the dynamics of dark energy in the context of cosmic evolution.
How does dark energy interact with matter in the universe?
Dark energy interacts with matter through its effect on the universe’s expansion. As dark energy drives the accelerated growth of the universe, it influences how matter, including galaxies and cosmic structures, is spaced out over time, a key area of study in understanding cosmic evolution.
What role do baryon acoustic oscillations play in dark energy research?
Baryon acoustic oscillations serve as a ‘standard ruler’ in measuring cosmological distances, helping researchers assess how dark energy has influenced the universe’s expansion at various points in time. This method is vital for accumulating evidence about the properties of dark energy.
Why is the study of dark energy significant in cosmology?
The study of dark energy is crucial because it directly relates to fundamental questions about the universe’s fate, its expansion rate, and the total energy content. Understanding dark energy’s properties and evolution will help scientists develop a more comprehensive picture of the cosmos.
What are the future directions for dark energy research?
Future dark energy research will focus on further analyzing the extensive datasets produced by DESI, refining models to account for evolving dark energy, and exploring new theoretical frameworks to better understand its role in cosmic evolution.
How can the public access data from the DESI dark energy project?
The DESI collaboration has made its Data Release 1 publicly available, allowing anyone to explore extensive data on millions of celestial objects. This open access supports diverse astrophysical research and increases public engagement with cosmology and the study of dark energy.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Dark Energy Overview | Dark energy is considered a driving force behind the universe’s accelerating expansion and is often seen as a ‘cosmological constant’. |
| New Findings | Recent research suggests that dark energy may be weakening over time, leading to reconsideration of the standard cosmological model. |
| Research Tools | The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) creates the largest 3D map of the universe to analyze dark energy’s influence on matter distribution. |
| Historical Analysis | The analysis spans 11 billion years, using Baryon Acoustic Oscillations to assess dark energy’s impact at various times. |
| Collaboration | Over 900 researchers from 70 institutions worldwide are involved in the DESI project, managed by the U.S. Department of Energy. |
| Availability of Data | The first data release from DESI is now available for public exploration, aiding various astrophysical research initiatives. |
| Future Research | The DESI survey continues to expand our understanding of cosmic structures and dark energy’s role in universe evolution. |
Summary
Dark energy is crucial in understanding the fate of our universe, as recent studies reveal that its influence may be changing. With contributions from the DESI collaboration, scientists are mapping dark energy’s impact on the cosmos, suggesting that the fundamental principles of cosmology might need an update. As ongoing research continues to unveil new data, the role of dark energy in driving the universe’s expansion remains a vital area of study, challenging our previous assumptions and reshaping our comprehension of the cosmic landscape.