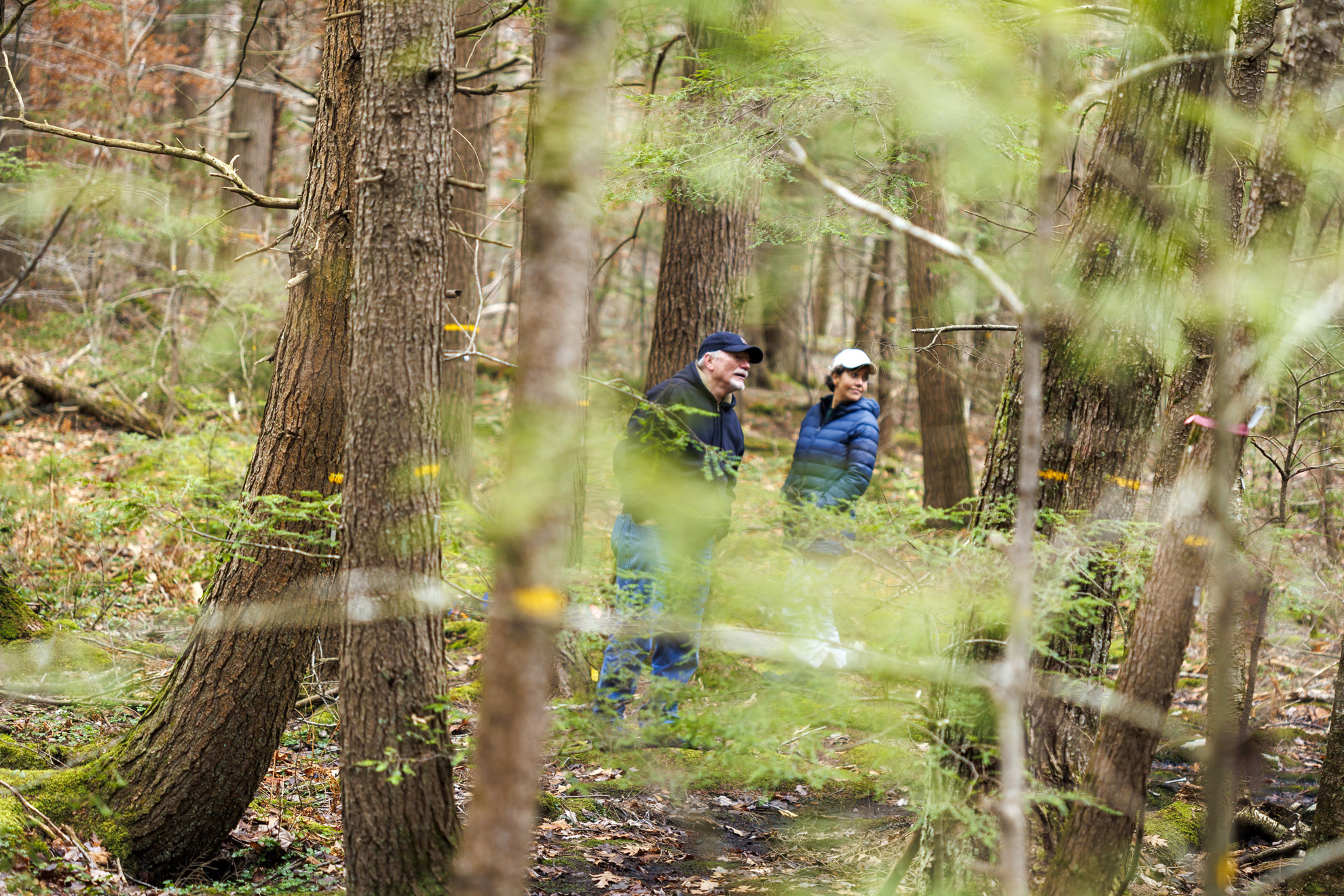
Climate change at Harvard Forest is more than just a scientific inquiry; it’s a poignant reminder of how our natural world is rapidly transforming. Nestled in Petersham, Massachusetts, this 4,000-acre forest serves as a critical laboratory for researchers like Emery Boose and Clarisse Hart, who are on the front lines studying the effects of warming winters and shifting ecosystems resilience. As they document changes in forest ecosystem dynamics, the implications of climate change become evident not only in data but also in the daily experiences of those who work there. With each passing season, the forest’s character morphs — from the invasive spread of pests to the surprising emergence of new species, all signaling a major shift in environmental challenges we face. The ongoing Harvard Forest research provides invaluable insight into how these ecological changes could shape our understanding of conservation and resilience in forest ecosystems.
The ongoing investigation into climate fluctuations at Harvard Forest underscores a pressing environmental narrative. Researchers are meticulously tracking alterations within this expansive woodland, which is not merely an academic endeavor but a crucial examination of nature’s adaptability amidst climate-related adversities. As ecological frameworks shift and species interactions evolve, the broader picture of environmental sustainability comes under scrutiny. This exploration not only highlights the impact of climate variability on ecosystems but also raises awareness of how human actions contribute to these changes. By delving into the complex interplay of factors at play, we begin to grasp the essential role forestry research plays in combating the effects of climate change.
Understanding Climate Change Through Harvard Forest Research
The Harvard Forest serves as a vital research hub for studying climate change and its impacts on forest ecosystems. Researchers at this site observe firsthand the shifts attributed to climate variables, such as temperature increases and altered precipitation patterns, that have been systematically documented since the 1960s. This long-term data collection provides invaluable insight into how ecosystems are adapting and reshaping in response to climate pressures. The researchers utilize innovative methodologies to understand these changes deeply, measuring ecosystem resilience and the health of different species within the forest.
As our planet experiences unprecedented transformations due to climate change, the Harvard Forest stands as a beacon for scientific exploration. Through detailed investigations and monitoring, scientists are uncovering the nuances of how individual species, such as the hemlock and black birch, respond to these environmental challenges. Insights gleaned from this research not only inform local conservation efforts but also contribute to broader dialogues on climate adaptation strategies necessary to sustain biodiversity and ecosystem services globally.
Ecosystem Resilience in the Face of Environmental Challenges
Ecosystem resilience is increasingly critical as environmental challenges intensify worldwide. At the Harvard Forest, researchers investigate how various species and ecological interactions help the forest adapt to changing climatic conditions. The decline of hemlocks, for instance, is being offset by the rise of black birches which, while altering the forest’s character, illustrate the dynamic nature of these ecosystems. This resilience implies that while species may shift, the forest continues to thrive through ecological succession, showcasing nature’s remarkable ability to adapt.
However, the loss of iconic species, such as hemlocks, can change the microclimates within the forest, affecting both soil chemistry and the hydrology of the ecosystem. This transformation leads to concerns about long-term ecological health and biodiversity. As researchers document these changes, they also explore adaptive management techniques to bolster resilience, ensuring that forest ecosystems can withstand ongoing climate shifts and maintain their ecological functions.
The Role of Long-term Data in Understanding Climate Trends
Long-term ecological data is a cornerstone of climate change research, allowing scientists to track and interpret trends over decades. At the Harvard Forest, records dating back to the 1830s provide an extensive backdrop against which climate change can be analyzed. This historical context is essential for understanding the variability of climate phenomena and the gradual shifts observed in forest composition and health. Such data enables scientists to assess the extent to which climate change influences species distribution, growth rates, and interactions among organisms.
Additionally, the unique wealth of historical climate data at the Harvard Forest means scientists can forecast potential future scenarios based on observed trends. By combining historical data with ongoing research, they can enhance predictive models which inform both conservation strategies and policy decisions. This evidence-based approach highlights how critical long-term monitoring is in shaping effective responses to climate change’s relentless advance.
Impacts of Invasive Species on Forest Ecosystems
Invasive species are a pressing concern for forest ecosystems, exacerbating the challenges posed by climate change. The introduction of pests such as the woolly adelgid has dramatically affected the health of hemlock trees in the Harvard Forest, leading to significant ecological shifts. As these trees decline, researchers observe not only the impact on local biodiversity but also alterations in forest dynamics, such as changes in light penetration and soil acidity, that affect understory vegetation.
The spread of invasive species is further complicated by climate change, as milder winters allow pests to thrive and expand their ranges. The Harvard Forest stands as a critical site for understanding these complex interactions, providing insights that can inform management strategies in impacted areas. By addressing the dual threats of climate change and invasive species, researchers aim to develop holistic approaches that promote ecosystem health and resilience.
Seasonal Changes and Their Effects on Forest Health
Seasonal changes are natural occurrences in forest ecosystems, but climate change is altering the predictable patterns that have sustained these environments for centuries. At the Harvard Forest, changing snowfall patterns and warming temperatures have led to delayed winter conditions, impacting the phenology of native species. Observations indicate that winters are shorter, with less severe cold and reduced snowpack, which can disrupt the life cycles of both plant and animal species dependent on these conditions.
These shifts in seasonal timing can create mismatches between flowering plants and their pollinators, ultimately impacting forest health and biodiversity. Research at Harvard Forest aims to illuminate these changing seasonal dynamics, enabling scientists to predict the cascading effects on species interactions and ecosystem stability. Understanding how these patterns evolve will be key in developing management approaches that support forest vitality amid climate change.
The Influence of Temperature on Forest Ecosystem Changes
Temperature plays a significant role in shaping forest ecosystems, particularly as global temperatures rise due to climate change. Within the Harvard Forest, scientists have documented trends indicating warmer winters and hotter summers, leading to altered growth patterns among tree species. For example, the successful infiltration of black birch has been observed as conditions become more favorable for temperate species that were once limited by cold winters.
The implications of elevated temperatures extend beyond individual species; they can affect soil microbial communities and nutrient cycling processes. By studying these changes, researchers at the Harvard Forest are gaining insights into how temperature influences forest structure and functions, equipping conservationists with the knowledge necessary to devise strategies that enhance biodiversity and ecosystem resilience in a warming world.
Community Engagement in Climate Change Research
Community engagement is essential in advancing climate change research, particularly in areas like the Harvard Forest, where local residents have a vested interest in the health of their natural surroundings. Researchers emphasize the importance of involving the community in their studies, as local knowledge and experiences contribute to a deeper understanding of environmental changes and an increased commitment to conservation initiatives. Engagement fosters a shared sense of stewardship for the landscape and encourages collaborative problem-solving.
Through educational programs and outreach efforts, the Harvard Forest team invites community members to participate in research activities, workshops, and guided tours. By fostering awareness and understanding of climate change’s impact on forest ecosystems, they empower residents to take action in their own backyards, thereby creating advocates for sustainability and resilience in the face of ongoing environmental challenges.
The Future of Ecosystem Management Amid Climate Change
As the impacts of climate change become more pronounced, the need for adaptive ecosystem management strategies intensifies. The Harvard Forest research team is at the forefront of investigating how to manage forested landscapes that must contend with rapid ecological shifts and invasive species. Their work focuses on developing frameworks that anticipate the future needs of forest ecosystems, enabling them to adapt effectively to new conditions while preserving biodiversity.
Future management strategies will need to integrate scientific findings with community input, as local stakeholders play a crucial role in implementing conservation efforts. Strategies may involve adaptive forestry techniques, habitat restoration initiatives, and increased public awareness campaigns to cultivate a culture of environmental stewardship. By prioritizing collaboration between science and community, the Harvard Forest aims to navigate the complexities of climate change while fostering resilient ecosystems.
Lessons Learned from the Harvard Forest Experience
The ongoing research at Harvard Forest presents numerous lessons regarding the intersection of climate change and forest ecosystems. One critical takeaway is the importance of long-term monitoring, which offers insights into trends that may not be apparent in short-term studies. This perspective is essential for developing effective conservation and management practices that consider both current and future climate scenarios.
Furthermore, the interplay between research and community engagement highlights the value of fostering public understanding and involvement in environmental issues. The Harvard Forest experience underscores that meaningful responses to climate change must encompass a shared commitment to preserving our natural heritage, ensuring that future generations inherit ecosystems rich in biodiversity and ecological function.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key findings from climate change research at Harvard Forest?
Harvard Forest research has highlighted significant changes due to climate change, including longer and warmer winters, a shift in tree species, and the impact of invasive pests like the woolly adelgid. Data collected over decades reveals a trend towards a warmer, wetter climate, leading to altered ecosystems and forest composition.
How is Harvard Forest studying the effects of climate change on forest ecosystems?
Harvard Forest employs around 100 ongoing research projects that examine various aspects of forest ecosystems resilience in the face of climate change. These studies include monitoring soil temperatures, gas exchange, and the effects of invasive species, providing critical insights into how forest ecosystems respond to environmental challenges.
What role do invasive pests play in Harvard Forest’s climate change research?
Invasive pests, particularly the woolly adelgid, are a focal point of climate change research at Harvard Forest. As climate conditions become milder, these pests thrive, threatening the health of hemlock trees, which are essential to the ecosystem. The research aims to understand their impact and explore potential resistance in local tree populations.
How has climate change impacted the biodiversity at Harvard Forest?
Climate change has led to a shift in biodiversity at Harvard Forest, with increasing populations of black birch replacing declining hemlocks. This transformation alters the forest’s microenvironment, nutrient flow, and overall ecosystem dynamics, demonstrating the resilience and adaptability of forest ecosystems under changing climate conditions.
What methods does Harvard Forest use to monitor climate change effects?
Harvard Forest utilizes a variety of research methods to monitor climate change effects, including long-term climate data collection, experimental plots for heating soil, and atmospheric gas exchange instruments. These diverse techniques allow researchers to assess changes in tree species composition, forest health, and ecosystem resilience.
Why is the research conducted at Harvard Forest important for understanding climate change?
Research at Harvard Forest provides invaluable data on the long-term impacts of climate change on forest ecosystems. By analyzing historical climate data alongside current trends, scientists can better predict future changes, inform conservation efforts, and enhance our understanding of how ecosystems adapt, which is crucial for managing environmental challenges.
What are the implications of shifting baselines in the context of climate change at Harvard Forest?
Shifting baselines refer to the changing perception of what constitutes a ‘normal’ forest ecosystem as climate change alters environmental conditions. At Harvard Forest, this concept underscores the need for continuous monitoring and education to ensure that future generations can appreciate the historical integrity of their ecosystems and the impacts of climate change.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Harvard Forest’s Location and Significance | The 4,000-acre Harvard Forest in Petersham, Massachusetts, serves as a climate change laboratory attracting global researchers. |
| Impact of Climate Change | The forest experiences changes such as warmer winters, increased light penetration, and the introduction of new species like black birch. |
| Long-Term Data Collection | Data on temperature and precipitation dating back to the 1960s helps identify climate trends amidst natural variability. |
| Ecosystem Changes | The decline of hemlocks due to the woolly adelgid has significant effects on the forest’s ecology, influencing soil chemistry and wildlife. |
| Research Initiatives | Around 100 research projects address the impacts of climate change on various ecological aspects through experimental plots. |
| Personal Experience Among Researchers | Researchers share personal observations that underline the profound changes and their emotional connections to the forest. |
| Future Generations | Concerns about shifting baselines highlight the impact of climate change on young people’s understanding of ecosystems. |
Summary
Climate change at Harvard Forest illustrates the profound and visible transformations occurring in this important ecosystem. Researchers like Emery Boose and Clarisse Hart observe firsthand the impacts of warmer winters, invasive species, and shifting flora. As climate change affects Harvard Forest, it sets an essential backdrop for understanding wider ecological changes, emphasizing the importance of environmental stewardship and the necessity of adapting conservation strategies to protect this cherished landscape.